Showing 1–12 of 110 results
- SKU:LLS-EXPLB-75-5-C1D2 | Web ID:2684Availability: 77 In Stock Ships 3-5 Days
- Watts: 75
- Lumens: 10500
- Lumens/Watt: 140
- Replaces: 400 Watt Metal Halide
- Color Temp: 5000K
- CRI: 70+
- IP Rating: IP66
- IK Rating: IK08
- Voltage: 100V-277V
- Surge Protection: 10kV
- Operating Temp: -40°F to 149°F
- Rated Life: 150,000 (L70) hours
- Dimmable: 1-10V
- Beam Angle (Std): 120°
- Optics: Tempered Glass Lens
- Fixture Color: Gray
- Mount: Yoke | 3/4 in NPT Pendant
- Mount (Opt): Surface | Wall
- Cord Length: No Cord
- Weight: 13 lbs
Starting At$485.00 - SKU:LLS-EXPLB-100-5-C1D2 | Web ID:2310Availability: 15 In Stock Ships 2-3 Days
- Watts: 100
- Lumens: 14000
- Lumens/Watt: 140
- Replaces: 400 Watt Metal Halide
- Color Temp: 5000K
- CRI: 70+
- IP Rating: IP66
- IK Rating: IK08
- Voltage: 100V-277V
- Surge Protection: 10kV
- Operating Temp: -40°F to 149°F
- Rated Life: 150,000 (L70) hours
- Dimmable: 1-10V
- Beam Angle (Std): 120°
- Optics: Tempered Glass Lens
- Fixture Color: Gray
- Mount: Yoke | 3/4 in NPT Pendant
- Mount (Opt): Surface | Wall
- Cord Length: No Cord
- Weight: 13 lbs
Starting At$555.00 - SKU:LLS-EXPLB-150-5-C1D2 | Web ID:2311Availability: 177 In Stock Ships 2-3 Days
- Watts: 150
- Lumens: 21000
- Lumens/Watt: 140
- Replaces: 400 Watt Metal Halide
- Color Temp: 5000K
- CRI: 70+
- IP Rating: IP66
- IK Rating: IK08
- Voltage: 100V-277V
- Surge Protection: 10kV
- Operating Temp: -40°F to 149°F
- Rated Life: 150,000 (L70) hours
- Dimmable: 1-10V
- Beam Angle (Std): 120°
- Optics: Tempered Glass Lens
- Fixture Color: Gray
- Mount: Yoke | 3/4 in NPT Pendant
- Mount (Opt): Surface | Wall
- Dimensions: 9.68 in H x 14.96 in D
- Cord Length: No Cord
- Weight: 20 lbs
Starting At$595.00 - SKU:LLS-EXPLB-200-5-C1D2 | Web ID:2682Availability: 67 In Stock Ships 3-5 Days
- Watts: 200
- Lumens: 28000
- Lumens/Watt: 140
- Replaces: 1000 Watt Metal Halide
- Color Temp: 5000K
- CRI: 70+
- IP Rating: IP66
- IK Rating: IK08
- Voltage: 100V-277V
- Surge Protection: 10kV
- Operating Temp: -40°F to 149°F
- Rated Life: 150,000 (L70) hours
- Dimmable: 1-10V
- Beam Angle (Std): 120°
- Optics: Tempered Glass Lens
- Fixture Color: Gray
- Mount: Yoke | 3/4 in NPT Pendant
- Mount (Opt): Surface | Wall
- Dimensions: 9.7 X 15 in
- Cord Length: No Cord
- Weight: 20 lbs
Starting At$635.00 - SKU:MLLG-E-LED-EXPLB-40-50-[V]-C1D2 | Web ID:1606100V-277V:Out of Stock277V-480V:Built to Order 6 Weeks
- Watts: 40
- Lumens: 5600
- Lumens/Watt: 140
- Replaces: 175 | 250 Watt Metal Halide
- Color Temp: 5000K
- CRI: 70+
- IP Rating: IP66
- IK Rating: IK10
- Voltage: 100V-277V | 277V-480V
- Surge Protection: 10kV
- Operating Temp: -40°F to 140°F
- Rated Life: 50,000 (L70) hours
- Dimmable: 1-10V
- Beam Angle (Std): 120°
- Beam Angle (Opt): 40° | 60° | 90°
- Optics: Tempered Glass Lens
- Fixture Color: Gray
- Mount: Yoke | 3/4 in NPT Pendant
- Dimensions: 7.09 x 9.09 in
- Weight: 8 lbs
Starting At$433.96 - SKU:MLLG-E-LED-EXPLB-60-50-[V]-C1D2 | Web ID:1609100V-277V:32 In StockShips 3-5 Days277V-480V:Built to Order 6 Weeks
- Watts: 60
- Lumens: 8400
- Lumens/Watt: 140
- Replaces: 250 Watt Metal Halide
- Color Temp: 5000K
- CRI: 70+
- IP Rating: IP66
- IK Rating: IK10
- Voltage: 100V-277V | 277V-480V
- Surge Protection: 10kV
- Operating Temp: -40°F to 140°F
- Rated Life: 50,000 (L70) hours
- Dimmable: 1-10V
- Beam Angle (Std): 120°
- Beam Angle (Opt): 40° | 60° | 90°
- Optics: Tempered Glass Lens
- Fixture Color: Gray
- Mount: Yoke | 3/4 in NPT Pendant
- Dimensions: 7.09 x 9.09 in
- Weight: 8 lbs
Starting At$528.30 - SKU:MLLG-E-LED-EXPLB-80-50-[V]-C1D2 | Web ID:1644100V-277V:938 In StockShips 3-5 Days277V-480V:Built to Order 6 Weeks
- Watts: 80
- Lumens: 11200
- Lumens/Watt: 140
- Replaces: 250 Watt Metal Halide
- Color Temp: 5000K
- CRI: 70+
- IP Rating: IP66
- IK Rating: IK10
- Voltage: 100V-277V | 277V-480V
- Surge Protection: 10kV
- Operating Temp: -40°F to 140°F
- Rated Life: 50,000 (L70) hours
- Dimmable: 1-10V
- Beam Angle (Std): 120°
- Beam Angle (Opt): 40° | 60° | 90°
- Optics: Tempered Glass Lens
- Fixture Color: Gray
- Mount: Yoke | 3/4 in NPT Pendant
- Dimensions: 10.63 X 10.47 in
- Weight: 9.7 lbs
Starting At$547.17 - SKU:MLLG-E-LED-EXPLB-80-50-C1D2-HT | Web ID:2302Built to Order 8 Weeks
- Watts: 80
- Lumens: 8000
- Lumens/Watt: 100
- Replaces: 250 Watt Metal Halide
- Color Temp: 5000K
- CRI: 70+
- IP Rating: IP66
- IK Rating: IK10
- Voltage: 120V
- Surge Protection: 10kV
- Operating Temp: -40°F to 176°F
- Rated Life: 50,000 (L70) hours
- Dimmable: No
- Beam Angle (Std): 120°
- Optics: Tempered Glass Lens
- Fixture Color: Gray
- Mount: Yoke | 3/4 in NPT Pendant
- Dimensions: 9.1 X 8.7 in
- Weight: 15 lbs
Starting At$786.20 - SKU:MLLG-E-LED-EXPLB-100-50-C1D2-HT | Web ID:2303Built to Order 8 Weeks
- Watts: 100
- Lumens: 10000
- Lumens/Watt: 100
- Replaces: 400 Watt Metal Halide
- Color Temp: 5000K
- CRI: 70+
- IP Rating: IP66
- IK Rating: IK10
- Voltage: 120V
- Surge Protection: 10kV
- Operating Temp: -40°F to 176°F
- Rated Life: 50,000 (L70) hours
- Dimmable: No
- Beam Angle (Std): 120°
- Beam Angle (Opt): 40° | 60° | 90°
- Optics: Tempered Glass Lens
- Fixture Color: Gray
- Mount: Yoke | 3/4 in NPT Pendant
- Dimensions: 14 in D X 11.3 in H
- Weight: 26 lbs
Starting At$1,109.30 - SKU:MLLG-E-LED-EXPLB-150-50-[V]-C1D2 | Web ID:1612100V-277V:256 In StockShips 3-5 Days277V-480V:30 In StockShips 3-5 Days
- Watts: 150
- Lumens: 21000
- Lumens/Watt: 140
- Replaces: 400 Watt Metal Halide
- Color Temp: 5000K
- CRI: 70+
- IP Rating: IP66
- IK Rating: IK10
- Voltage: 100V-277V | 277V-480V
- Surge Protection: 10kV
- Operating Temp: -40°F to 140°F
- Rated Life: 50,000 (L70) hours
- Dimmable: 1-10V
- Beam Angle (Std): 120°
- Beam Angle (Opt): 40° | 60° | 90°
- Optics: Tempered Glass Lens
- Fixture Color: Gray
- Mount: Yoke | 3/4 in NPT Pendant
- Dimensions: 14.56 X 11.4 in
- Weight: 18.1 lbs
Starting At$650.94 - SKU:MLLG-E-LED-EXPLB-150-50-C1D2-HT | Web ID:2304Built to Order 8 Weeks
- Watts: 150
- Lumens: 15000
- Lumens/Watt: 100
- Replaces: 400 Watt Metal Halide
- Color Temp: 5000K
- CRI: 70+
- IP Rating: IP66
- IK Rating: IK10
- Voltage: 120V
- Surge Protection: 10kV
- Operating Temp: -40°F to 176°F
- Rated Life: 50,000 (L70) hours
- Dimmable: No
- Beam Angle (Std): 120°
- Beam Angle (Opt): 40° | 60° | 90°
- Optics: Tempered Glass Lens
- Fixture Color: Gray
- Mount: Yoke | 3/4 in NPT Pendant
- Dimensions: 14 X 11.3 in
- Weight: 28 lbs
Starting At$1,179.10 - SKU:MLLG-E-LED-EXPLB-200-50-[V]-C1D2 | Web ID:1643100V-277V:355 In StockShips 3-5 Days277V-480V:Built to Order 6 Weeks
- Watts: 200
- Lumens: 28000
- Lumens/Watt: 140
- Replaces: 400 Watt Metal Halide
- Color Temp: 5000K
- CRI: 70+
- IP Rating: IP66
- IK Rating: IK10
- Voltage: 100V-277V | 277V-480V
- Surge Protection: 10kV
- Operating Temp: -40°F to 140°F
- Rated Life: 50,000 (L70) hours
- Dimmable: 1-10V
- Beam Angle (Std): 120°
- Beam Angle (Opt): 40° | 60° | 90°
- Optics: Tempered Glass Lens
- Fixture Color: Gray
- Mount: Yoke | 3/4 in NPT Pendant
- Dimensions: 14.56 X 11.4 in
- Weight: 18.1 lbs
Starting At$703.70
What Are Explosion Proof Lights and Why Your Facility Needs Them
Explosion proof light fixtures, also called hazardous area lighting, are engineered to contain and prevent explosions in industrial environments where flammable gases, liquids, or combustible dust create ignition risks.
What makes a light "explosion proof"? These fixtures are built to control any internal explosion and prevent it from igniting the surrounding atmosphere. Explosion proof LED lights also eliminate the risk of sparks that could ignite flammable materials, enhancing safety in hazardous areas.
The critical difference: Standard lights can become ignition sources. Explosion proof lights are engineered to operate safely even if component failures occur inside the fixture. Modern designs use LEDs for energy efficiency and durability in extreme environments.
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) provides comprehensive guidance on electrical safety in hazardous locations, emphasizing that proper classification and equipment selection are critical to preventing workplace explosions and protecting workers. OSHA's standards for hazardous locations detail the requirements for electrical installations in areas where flammable gases, vapors, liquids, or combustible dusts may be present.
Quick Selection Guide
- Class I (gas/vapor hazards): Use for petroleum refineries, paint booths, chemical plants - verify Group D for gasoline/propane, Group C for ethylene
- Class II (dust hazards): Use for grain processing, flour mills, coal facilities - confirm Group G for agricultural dust, Group F for coal dust
- Division 1: Required when hazards are present continuously during normal operation - higher safety rating needed
- Division 2: Used when hazards are only present during equipment failure or abnormal conditions - Division 1 fixtures acceptable substitute
- UL844 certification required: Verify all fixtures carry proper Class/Division/Group ratings for your specific hazardous materials
- Installation requirements: Must use certified electricians, explosion-rated conduit, and proper seal-offs per NEC 501
Tip: Never use Division 2 fixtures in Division 1 areas or mix certified and non-certified components - every electrical component needs a proper hazardous location rating.
Use When / Don't Use When
Use LED Explosion Proof Lights When
- Hazardous materials are present - flammable gases, vapors, liquids, or combustible dust create ignition risks
- NEC classification applies - facility has been assessed as Class I, II, or III hazardous location
- OSHA compliance required - workplace safety regulations mandate explosion-rated equipment
- Energy efficiency matters - need 50-75% energy reduction compared to HID with 100,000+ hour lifespan
- Extreme conditions exist - high temperatures, moisture, vibration, corrosive atmospheres, or chemical exposure
Don't Use an LED Explosion Proof Light When
- Non-hazardous environments - residential, office, or standard commercial areas with no ignition risks
- Unclassified industrial areas - manufacturing spaces with no flammable materials or combustible dust
- Budget doesn't support proper installation - certified electricians and explosion-rated components required
- Classification uncertain - haven't completed a professional hazardous area assessment to determine actual requirements
What We Verify Before You Order Explosion Proof LED Light Fixtures
We confirm
- Hazardous location classification (Class I/II, Division 1/2, Group A-G)
- Environmental conditions (temperature, moisture, vibration, chemicals)
- Mounting requirements and fixture spacing needs
- Electrical specifications and conduit system compatibility
If we provide a lighting plan, you will get
- Fixture layout with proper spacing calculations for uniform illumination
- Lumen output specifications and color temperature recommendations
- Installation guidelines
Note: Guidance is general planning information. Final selection should be validated with a photometric plan and confirmed by a licensed professional when required for code- or safety-critical areas.
Applications & Industries That Require Explosion Proof Lighting
Chemical Processing, Manufacturing & Storage
Chemical processing plants |
Explosion proof lighting is required in chemical processing facilities where flammable gases, vapors, or reactive compounds are present. Certified fixtures reduce ignition risks and support safe operations across production, blending, and handling areas. |
Chemical storage warehouses and tank farms |
Hazardous vapors from stored chemicals need explosion proof lighting to prevent ignition during material handling, inspections, and routine maintenance. |
Paint spray booths and finishing areas |
Paint fumes and solvent vapors require Class I Division 1 or Division 2 explosion proof lighting to eliminate ignition sources and maintain compliance with safety codes. |
Pharmaceutical manufacturing facilities |
Solvent-based processes and volatile compounds used in pharmaceutical production require hazardous location lighting to maintain controlled, ignition-safe environments. |
Oil, Gas & Petrochemical Facilities
Oil refineries and petrochemical plants |
High concentrations of flammable hydrocarbons make explosion proof LED lighting essential for preventing catastrophic ignition events in refining and processing areas. |
Offshore oil and gas platforms |
Marine environments combined with combustible gases require corrosion-resistant explosion proof fixtures that deliver reliable illumination under extreme conditions. |
Natural gas processing and compressor stations |
Explosion proof lighting protects personnel and equipment in areas where pressurized gas systems and leaks can create hazardous atmospheres. |
Food, Beverage & Agricultural Processing
Grain elevators and grain handling facilities |
Combustible grain dust accumulation requires Class II explosion proof lighting to reduce the risk of dust ignition and secondary explosions. |
Food processing plants |
Facilities handling sugar, flour, starch, or other combustible food ingredients require dust ignition-proof lighting to maintain safe production environments. |
Distilleries and alcohol production facilities |
Ethanol vapors generated during fermentation and distillation processes necessitate explosion proof lighting to prevent fires and equipment damage. |
Industrial Manufacturing & Heavy Industry
Manufacturing plants with hazardous locations |
Explosion proof lighting is required in manufacturing environments where flammable gases, vapors, or combustible dusts are present during production or finishing operations. |
Metal finishing and coating facilities |
Processes involving solvents, degreasers, and coatings require hazardous location lighting to eliminate ignition risks. |
Paper mills and wood processing plants |
Fine wood dust and chemical treatments create combustible atmospheres where explosion proof fixtures improve safety and reliability. |
Mining operations (underground and surface) |
Methane gas and coal dust present explosion hazards that require specialized, certified lighting solutions for safe mining operations. |
Water, Wastewater & Utilities
Wastewater treatment plants |
Methane and hydrogen sulfide gases produced during treatment processes require explosion proof lighting in digesters, pump stations, and enclosed areas. |
Water treatment and pumping stations |
Hazardous gases in confined utility spaces necessitate certified hazardous location lighting to ensure safe maintenance and operation. |
Energy Storage & Emerging Technologies
Battery energy storage systems (BESS) |
Explosion proof lighting is increasingly required in lithium-ion battery storage facilities where off-gassing and thermal runaway pose ignition risks. |
Hydrogen production and storage facilities |
Hydrogen's low ignition energy demands explosion proof lighting designed for high-risk gas environments. |
Explosion proof LED lighting is used in laboratories, refineries, fabrication workshops, food and beverage facilities, and other locations with extreme conditions such as high temperatures, moisture, and vibrations.
Our customer replaced explosion proof fluorescent fixtures with our 100 Watt 4 Foot Explosion Proof Linear LED Light | 16000 Lumens linear fixtures. They experienced a dramatic improvement in light quality when they converted over to LED
Case Study: Conversion of existing lighting to LED Lighting Supply Class 1 Division 2 Fixtures in Holbrook, AZ
|
After: 200 Watt Square Explosion Proof LED Light | 28000 Lumens |
After: 200 Watt Square Explosion Proof LED Light | 28000 Lumens |
 |
 |
Lighting Plan We Created for the Customer
|
Lighting Plan |
Heat Map |
 |
 |
Explosion Proof Lighting Installation Plan Metrics
- Mounting height: 20 ft
- Fixture Used: MLLG-E-LED-EXPLA-200-50-[V]-C1D2: 200 Watt Square Explosion Proof LED Light | 28000 Lumens | Class 1 Div 2 | Class 2 Div 2 | 5000K | 100V-277V or 277V-480V
- FC achieved: 62.80 FC average
- Uniformity (Avg/Min): 1.85
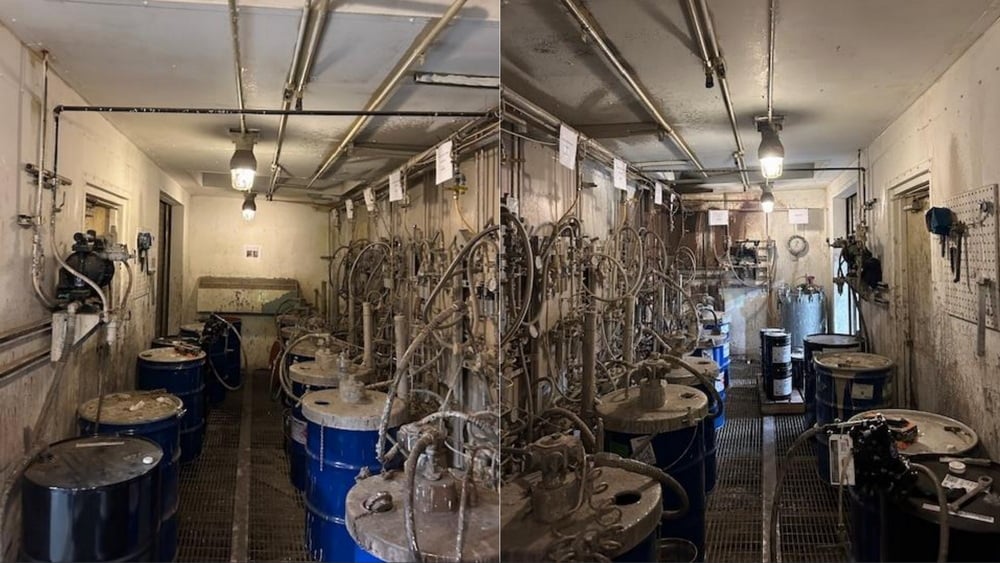
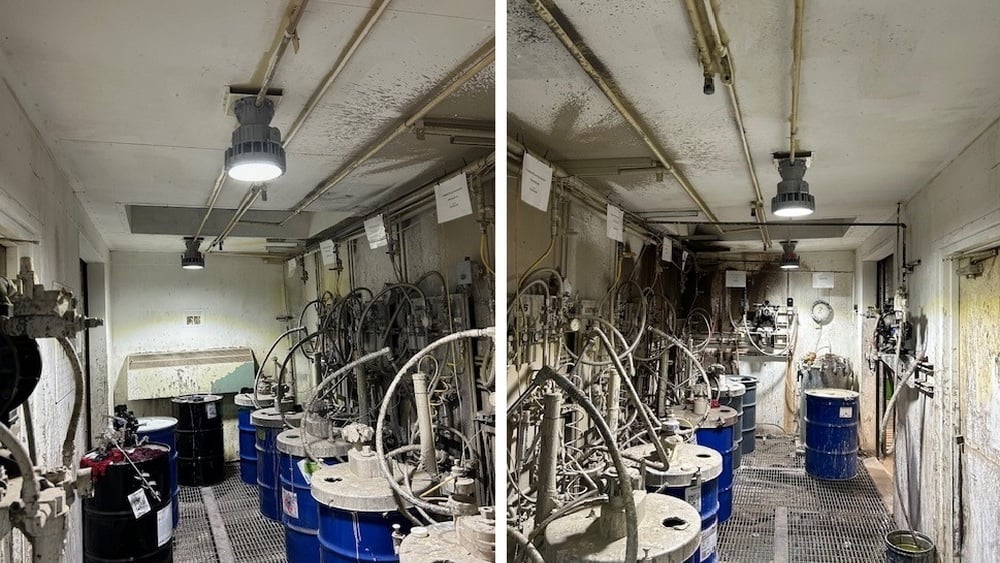
Case Study: Conversion of existing paint booth metal halide explosion proof lighting to LED Lighting Supply Class 1 Division 1 Fixtures in Chicago, IL
|
Before: 100 Watt Round Explosion Proof Metal Halide Light |
After: 50 Watt Round Explosion Proof LED Light | 7000 Lumens |
 |
 |
Lighting Plan We Created for the Customer
|
Lighting Plan |
Heat Map |
 |
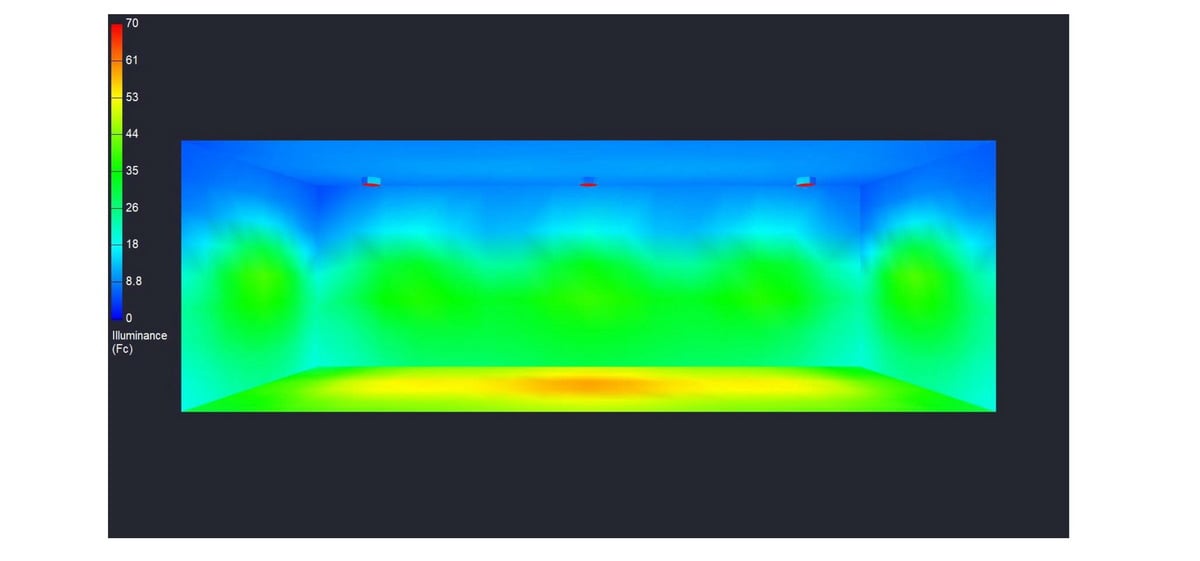 |
Explosion Proof Lighting Installation Plan Metrics
- Mounting height: 10 ft
- Fixture Used: LLS-EXPLC-50-5-C1D1: 50 Watt Round Explosion Proof LED Light | 7000 Lumens | Class 1 Div 1 | 5000K | 100-277V
- FC achieved: 53.54 FC average
- Uniformity (Avg/Min): 1.59
How to Determine If Your Location Requires Explosion Proof Lighting
The industry standard process involves evaluating your facility using the NEC hazardous location classification system. Non-hazardous areas, such as residential or office environments, typically do not require explosion proof lighting, as the risk of explosion or fire is minimal. In these locations, standard lighting options are usually sufficient.
The National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) establishes the foundational standards for hazardous location classification through NFPA 70, the National Electrical Code (NEC). The NEC provides comprehensive guidelines for determining proper electrical equipment ratings based on the type and concentration of hazardous materials present in industrial environments.
Always consult with a professional who has expertise in explosion proof lights to help determine the proper class of your space.
LED Lighting Supply's 3-Step Classification Process
Expert methodology for determining explosion proof lighting requirements
STEP 1: IDENTIFY HAZARDOUS MATERIAL PRESENCE TYPE - What hazardous materials are present? (Categories)
| Class I | Flammable gases, vapors, or liquids Examples: Gasoline, acetylene, ethylene |
| Class II | Combustible dust (=420 microns) Examples: Grain dust, coal dust, metal dust |
STEP 2 - DETERMINE PRESENCE FREQUENCY - How often are materials present? (Divisions)
| Division 1 | Present continuously or frequently during normal operating conditions Risk Level: HIGH |
| Division 2 | Present only during abnormal conditions or equipment failure Risk Level: MODERATE |
STEP 3 - SELECT GROUP CLASSIFICATION - What specific material group applies?
| Class I Groups | Group A: Acetylene Group B: Hydrogen Group C: Ethylene Group D: Gasoline/Propane |
| Class II Groups | Group E: Electrical-conductive dust Group F: Carbonaceous dust Group G: Agricultural/polymer dust |
| Class III Groups | No group classifications Evaluated case-by-case |
Explosion Proof / Hazardous Location Lighting Selector
Common Hazardous Location Classifications by Industry
Reference guide for typical explosion-proof lighting requirements subject to site conditions
| Petroleum Refineries | Class I, Division 1 & 2 Group D: Gasoline vapors, petroleum products |
| Chemical Processing Plants | Class I, Division 1 & 2 Group C, D: Ethylene, acetylene, and various chemicals |
| Paint Spray Booths | Class I, Division 1 Group D: Paint solvents, volatile organic compounds |
| Grain Storage/Processing | Class II, Division 1 & 2 Group G: Agricultural dust, grain particles |
| Coal Processing Facilities | Class II, Division 1 & 2 Group F: Coal dust, carbonaceous materials |
| Aircraft Hangars | Class I, Division 2 Group D: Aviation fuel vapors |
| Gasoline Dispensing Areas | Class I, Division 1 & 2 Group D: Gasoline vapors |
| Underground Coal Mines | Class I & II, Division 1 Group C, F: Methane gas, coal dust |
| Flour Mills | Class II, Division 1 & 2 Group G: Flour dust, grain particles |
| Wood Processing Plants | Class II, Division 2 Group G: Wood dust, sawdust |
| Textile Manufacturing | Class III, Division 1 & 2 No Groups: Cotton fibers, synthetic materials |
| Wastewater Treatment | Class I, Division 2 Group D: Methane, hydrogen sulfide |
| Distilleries | Class I, Division 1 & 2 Group D: Alcohol vapors, ethanol |
| Metal Processing | Class II, Division 2 Group E: Metal dust, conductive particles |
| Pharmaceutical Manufacturing | Class I, Division 2 Group D: Solvent vapors, chemical processes |
Important: These are typical classifications only. Each facility requires individual assessment by qualified professionals to determine exact hazardous area boundaries and appropriate fixture requirements.
How to Select the Right Explosion Proof Lighting Solution for Your Project
The ideal option is to consult an experienced lighting professional who understands both safety requirements and application-specific needs. It is crucial to select fixtures that provide proper illumination in hazardous environments to ensure safety and durability.
Our Proven Selection Process
| Site Assessment and Classification Verification | Confirm hazardous area classifications Identify environmental conditions Evaluate mounting requirements |
| Lighting Design and Layout Planning | Calculate proper fixture spacing Determine appropriate lumen outputs Select optimal color temperatures (typically 5000K for industrial settings) |
| Compliance and Installation Planning | Verify UL certification requirements. This means the fixtures meet the necessary safety standards for hazardous environments. Plan conduit and junction box specifications |
Quick Reference: Division 1 fixtures can substitute for Division 2 applications within the same class and group when properly specified, but never use lower-rated fixtures in higher-classification areas.
LED Lighting Supply's Explosion Proof Lighting Advantages
Energy Efficiency & Durability
Our explosion proof LED fixtures are highly efficient and consume much less energy than traditional lighting, delivering 50-75% energy reduction depending on model compared to traditional HID lighting.
100,000+ hour lifespans eliminate frequent bulb and ballast replacements, reducing maintenance costs and minimizing personnel exposure in hazardous areas.
Our explosion proof fixtures are engineered to withstand extreme hazardous location conditions, including:
- High temperature variations
- Moisture and corrosive atmospheres
- Vibration and impact exposure
- Flying debris and harsh chemicals
- LEDs generate less heat, which enhances safety and performance in hazardous environments
What are the Cost Savings and ROI When You Convert from Metal Halide to LED?
60W LED Explosion Proof Light vs 250W Metal Halide Replacement (with ballast)
Assumptions: Based on 24 hours/day, 365 days/year at $0.16/kWh,
20 fixture(s), and a 15% ballast factor applied to the metal halide wattage
(250W lamp + 15% ballast = ~ 288W input).
•
Energy cost and ROI calculations are based on energy savings only and assume an LED fixture cost of
$415.00 per fixture.
• Maintenance savings from reduced bulb and ballast replacements are not included
in these calculations.
| Metal Halide (288W per fixture) |
Annual Energy Cost (per fixture): $402.96 Annual Energy Cost (all 20 fixtures): $8,059.20 5 Year Energy Cost (all fixtures): $40,296.00 5 Year Savings (all fixtures): $0.00 |
| LED Explosion Proof Light (60W per fixture) |
Annual Energy Cost (per fixture): $84.10 Annual Energy Cost (all 20 fixtures): $1,681.92 5 Year Energy Cost (all fixtures): $8,409.60 5 Year Savings (all fixtures): $31,886.40 |
| Savings & Payback |
Single Fixture Annual Savings (energy only): $318.86 20 Fixture Annual Savings (energy only): $6,377.28 LED Fixture Project Cost (20 fixtures): $8,300.00 Simple Payback from Energy Savings Only: under 16 months |
| Performance Summary |
Energy Reduction: 79% 5-Year ROI (All Fixtures, Energy Only): 284% Lamp Life: 50,000+ (LED) vs 15,000 (MH) |
In this example with 20 fixture(s), total LED fixture investment is approximately $8,300.00, and estimated annual energy-only savings are $6,377.28. Simple payback based on energy savings alone is under 16 months. Maintenance savings from eliminating metal halide bulb and ballast replacements provide additional value throughout the fixture's 50,000-hour lifespan, but are not included in this ROI calculation.
The U.S. Department of Energy has extensively documented the energy savings potential of LED lighting in industrial applications, noting that LED technology can reduce energy consumption by 50% or more compared to conventional lighting technologies. The DOE's Solid-State Lighting program demonstrates how LED adoption in industrial settings contributes to significant operational cost reductions and improved workplace safety through better light quality and reduced heat generation.
Our 40 Watt Explosion Proof Jelly Jar LED Light | 5200 Lumens was installed to replace old halogen jelly jar lights.
Superior Safety Performance
- UL tested and certified per listed certifications to meet the highest standards in explosive atmospheres
- Instant-on performance eliminates warm-up delays
- Cool-running operation reduces surface temperatures compared to traditional metal halide alternatives
How to Install Explosion-Proof Lights
Always use qualified electricians. Explosion proof installations require certified electricians. All components (conduit, junction boxes, switches) must carry appropriate hazardous location ratings.
| Follow NEC Article 500-505 Guidelines | Use explosion-rated conduit systems Install proper grounding and bonding Maintain required seal-off distances Document all installation specifications |
| Avoid These Common Installation Mistakes: | Using standard electrical whips or cords Mixing rated and non-rated components Improper seal-off installation Inadequate grounding systems |
Explosion Proof Certifications & Compliance
All explosion proof lighting fixtures offered by LED Lighting Supply carry certifications for hazardous location use in accordance with applicable safety standards.
- UL844 certified for Class I, II, and III hazardous locations in North America
- ATEX and IECEx certified options available for international and zone-based applications
Not sure which certification or classification applies to your facility? See our Hazardous Location Lighting Buyer's Guide for a full breakdown of NEC vs ATEX standards, zones, divisions, and substance types.
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
After 15+ years in hazardous location installations, we keep seeing facilities make the same dangerous mistakes with explosion proof lighting. Most problems come from treating these installations like regular industrial jobs without understanding the unique safety requirements.
- Assuming Division 2 fixtures work for Division 1 applications because they're almost the same. Division ratings are absolute and non-negotiable.
- Forgetting to torque fixture covers to the manufacturer's specifications. Loose covers compromise the explosion containment and void certifications.
- The conduit runs too long between seal-offs. Maximum distances are specified in code and cannot be exceeded, even by a few feet.
- Failing to properly ground and bond all metallic components. Poor grounding creates static discharge risks in explosive atmospheres.
- Installing fixtures before verifying the actual hazardous area boundaries. What looks like Division 2 might actually be Division 1, depending on ventilation and process conditions.
LED Explosion Proof Lights for Hazardous Locations Frequently Asked Questions
What are explosion proof lights and how do they work?
Explosion proof light fixtures are engineered safety systems designed to contain and prevent explosions in environments where flammable gases, vapors, liquids, or combustible dust create ignition risks. Unlike standard lighting, these fixtures control any internal explosion and prevent it from igniting the surrounding atmosphere.
What industries require explosion proof lighting?
Industries with flammable gases or combustible dust require explosion proof lighting, including petroleum refineries, chemical plants, grain processing facilities, paint spray booths, mining operations, distilleries, and wastewater treatment plants. Each facility requires individual assessment to determine exact hazardous area boundaries.
What is the difference between Class I and Class II hazardous locations?
Class I locations contain flammable gases, vapors, or liquids such as gasoline, acetylene, or ethylene. Class II locations contain combustible dust 420 microns or smaller, such as grain dust, coal dust, or metal dust.
What is the difference between Division 1 and Division 2?
Division 1 applies when hazards are present continuously or frequently during normal operation and requires a higher safety rating. Division 2 applies when ignitable concentrations are unlikely during normal operation and hazards only present during equipment failure or abnormal conditions.
Can Division 2 fixtures be used in Division 1 areas?
No. Division 1 fixtures can substitute for Division 2 applications within the same class and group, but Division 2 fixtures must never be used in Division 1 areas. Division ratings are absolute and non-negotiable.
What certifications should explosion proof lights have?
All fixtures must carry UL844 certification for Class I, II, and III hazardous locations in North America. Verify fixtures carry proper Class, Division, and Group ratings for your specific hazardous materials. ATEX and IECEx certified options are available for international and zone-based applications.
How much energy do LED explosion proof lights save compared to HID?
LED explosion proof fixtures deliver 50-75% energy reduction compared to traditional HID lighting, depending on model. LEDs also generate less heat, which enhances safety and performance in hazardous environments.
How long do LED explosion proof lights last?
LED explosion proof fixtures have 100,000+ hour lifespans, eliminating frequent bulb and ballast replacements. This reduces maintenance costs and minimizes personnel exposure in hazardous areas.
What environmental conditions can explosion proof lights withstand?
Explosion proof fixtures are engineered to withstand high temperature variations, moisture and corrosive atmospheres, vibration and impact exposure, flying debris, and harsh chemicals.
What are the installation requirements for explosion proof lighting?
Installation requires certified electricians, explosion-rated conduit, and proper seal-offs per NEC 501. Every electrical component in the path needs a proper hazardous location rating - mixing certified and non-certified components is not acceptable.
What are common installation mistakes to avoid?
Common mistakes include using standard whips instead of rigid conduit, mixing certified and non-certified components, installing seal-offs in wrong locations, and failing to properly ground and bond all metallic components. Poor grounding creates static discharge risks in explosive atmospheres.
How do I determine if my facility needs explosion proof lighting?
Facilities require explosion proof lighting when flammable gases, vapors, liquids, or combustible dust create ignition risks and the location has been assessed as a Class I, II, or III hazardous location under NEC classification. Final selection should be validated with a photometric plan and confirmed by a licensed professional when required for code- or safety-critical areas.






















